Ohio Higher Education Under Scrutiny: Affordability Gaps and Policy Shortcomings
The issue of affordable higher education in Ohio has taken center stage recently as new research unveils that earning a bachelor’s degree at public universities in the state comes with a significantly higher price tag compared to other Great Lakes states. While community colleges in Ohio have shown more promise as a reasonably priced option, the overall affordability gap for four-year institutions is alarming, with students facing a daunting burden that can be off-putting, overwhelming, and even nerve-racking.
This editorial explores the root causes of these cost gaps, examines state funding challenges, and probes into potential strategies by which Ohio might better support those who aim to earn a bachelor’s degree. In doing so, we will take a closer look at the tricky parts of academic finance, the tangled issues in state funding, and the confusing bits of policy decisions that ultimately affect students and families alike.
Ohio’s Public University Costs: When Tuition Becomes a Barrier
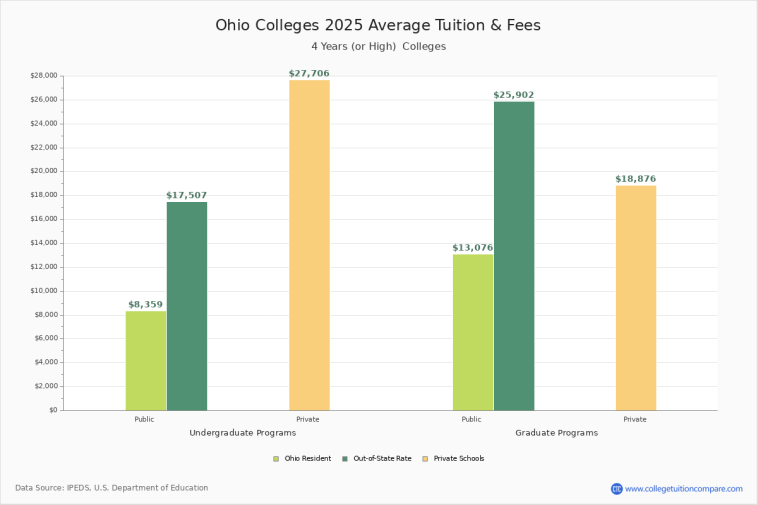
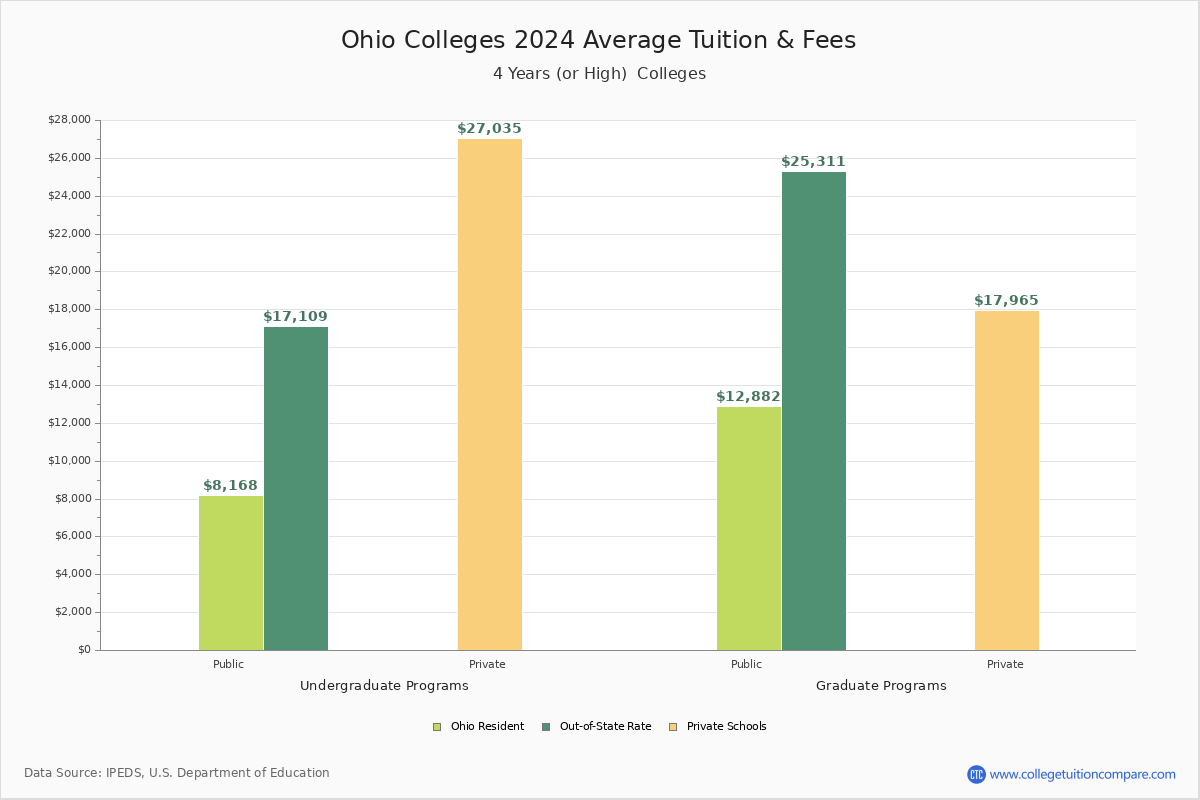
Recent findings from the National College Attainment Network (NCAN) reveal that students enrolled in Ohio’s 14 public four-year institutions face an average affordability gap of $5,138. This gap – the difference between tuition costs and what students can actually afford to pay through financial aid, scholarships, and loans – is more than three times the national average of $1,555, and significantly higher than those experienced in Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin.
In practical terms, this means that many students from low- and middle-income households are caught in a situation laden with problems when it comes to pursuing a four-year degree. The gap represents not just a numerical cost but also an intimidating financial barrier that puts students at a disadvantage before they’ve even begun their academic journey.
To better understand how this happens, we can break down the components of the issue:
- Tuition Increases: Rising tuition fees outpace the growth of student financial aid programs.
- Limited Grants and Scholarships: A slow growth in state-funded programs means fewer resources available for need-based aid.
- Dependence on Loans: As the gap widens, students are forced to rely on federal student loans, which further burdens them with debt.
These factors collectively create an environment in which finances become a major, if not the most, influencing factor in educational pursuits.
Community Colleges Provide an Affordable Alternative
While the affordability gap at four-year public universities is a grave concern, Ohio’s 22 public community colleges offer an alternative that many might overlook. According to the NCAN study, over 70% of these institutions meet the definition of affordability. In essence, the total cost paid by in-state full-time students (including a modest emergency fee) is less than or equal to the sum of scholarships, grants, federal student loans, and other contributions received.
This comparatively favorable picture for community colleges suggests that, despite the challenges, there is still hope for a more accessible higher education pathway in Ohio. However, it is critical not to mistake the benefits of community colleges for a one-size-fits-all solution; the savings come with clear warnings that the long-term economic advantages of a bachelor’s degree can be significant.
Some important points to highlight about Ohio’s community colleges include:
- Cost Efficiency: Lower tuition rates help minimize the immediate economic strain on students and their families.
- Accessibility: Community colleges often offer flexible scheduling and varied programs that cater to non-traditional and first-generation college students.
- Transfer Potential: Many institutions have articulation agreements with four-year universities, allowing students to transfer credits and eventually complete a bachelor’s degree.
While community colleges are a bright spot in an otherwise challenging landscape, it is clear that there are still hidden complexities in the broader pattern of higher education funding that need to be addressed.
State Funding and the Hidden Complexities of Higher Education Finance
One key factor contributing to these affordability challenges is the limited state investment in higher education. Over the past two decades, Ohio has lagged behind the national average in state and local support for its public colleges and universities. Though recent budgets have included modest boosts in funding – along with enhanced need-based scholarship programs – these measures have not been enough to bridge the affordability gap completely.
Some of the fine points that illustrate these tangled issues include:
- Budget Cuts Versus Increases: While some states in the Great Lakes region have increased their investment in higher education, Ohio has seen only slight boosts, leaving a notable discrepancy in educational quality and affordability.
- Tuition Revenue Dependency: Many Ohio institutions rely heavily on tuition revenue to balance their budgets, which in turn drives tuition fees higher and exacerbates affordability issues.
- Economic Realities: The demand for financial aid has grown, and the rising cost of living has made the existing financial aid packages less effective in covering the real cost of a college education.
It is evident that the state’s policy choices are ripe with a number of small distinctions—those little twists that, if addressed, could lead to more equitable funding in the long run. When policymakers fail to find your way through these challenging parts, the overall system remains skewed against students from less affluent backgrounds.
Comparing Financial Structures across the Great Lakes Region
The situation in Ohio is not happening in isolation. Across the Great Lakes states, there is a marked difference in how education is valued and funded. Specifically, Ohio’s enormous affordability gap stands out starkly when compared to states like Illinois, which has made bigger strides in both funding and facilitating the free application process for federal student aid.
Let’s examine some of the key differences:
| State | Average Affordability Gap | Level of State Support | Tendency to Rely on Tuition Revenue |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ohio | $5,138 | Below National Average | High Reliance |
| Illinois | Significantly Lower than Ohio | Higher Investments | Moderate Reliance |
| Indiana/Michigan/Minnesota/Wisconsin | Lower than Ohio’s Gap | Varied, but trending higher than Ohio | Moderate to Low Reliance |
These head-to-head comparisons emphasize how the small details of state policy—those surprising twists and turns in funding decisions—can result in dramatically different experiences for students seeking higher education.
Personal Stories: The Hidden Cost for Students and Their Families
Beyond the numbers and statistics are the personal stories of students who find themselves in a precarious financial position. Imagine a first-generation college student who must sort out the competing demands of academic success and financial survival. Every semester, they face the overwhelming challenge of not only keeping up with rigorous academic requirements but also finding a way to pay for tuition, books, and living expenses.
The human cost of this affordability gap should not be underestimated. For many, the need to work part-time or even full-time while studying can lead to a nerve-racking juggling act of responsibilities. The resulting stress can affect academic performance, mental health, and overall quality of life.
A few points to consider regarding these personal trials include:
- Employment to Bridge the Gap: Many students resort to taking on extra work, which diverts precious time and energy away from their studies.
- Reliance on Debt: The necessity of private loans leads to significant debt accumulation, affecting long-term financial security.
- Family Pressure: In many cases, students also feel the burden of family expectations and the need to contribute financially at home, complicating their academic progress.
These everyday stories dig into the heart of the problem, showing how the issue is not a distant policy debate but a lived reality for countless Ohio families. Each individual story is a microcosm of the broader challenges facing the state’s higher education system.
Learning Lessons from Illinois: How Policy Can Make a Difference
While Ohio struggles with unaffordable tuition fees and an intimidating financial gap, there are states in the Great Lakes region that have managed to tighten the budget bridge for college students. Illinois is one such example. By significantly increasing state funding for higher education and actively promoting FAFSA completion, Illinois has taken practical steps that have resulted in lower average affordability gaps.
Ohio policymakers might consider the following strategies inspired by Illinois’s approach:
- Increase Funding: A steady increase in state investments can ease some of the reliance on tuition as the primary revenue source for institutions.
- Boost Financial Aid Programs: Expanding need-based scholarships and grants can help close the affordability gap.
- Promote Federal Aid Enrollment: Encouraging more students to complete the FAFSA can unlock additional federal aid resources, lightening the financial load.
These recommendations are not a cure-all but represent actionable steps that may provide some relief. If Ohio leaders can find their path through these small distinctions in policy, they might be able to create a more supportive environment for students statewide.
State Investment: The Key to Reinventing Higher Education Affordability
One of the most critical—and super important—factors that can influence the future of Ohio’s higher education landscape is state investment. For decades, public funding for higher education has been one of the trickiest parts of the cost equation. The lack of robust funding options has led to a scenario where many institutions must rely more heavily on tuition revenue, subsequently increasing the financial burden on students.
If Ohio wants to bolster its higher education system, it must prioritize increased state and local contributions. Key actions in this realm could include:
- Long-Term Budgeting: Establishing a long-term plan for higher education funding that provides stability and predictability.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Leveraging private sector investments and donations to supplement state funding, creating a more diverse revenue stream.
- Reviewing Financial Aid Policies: Regularly revisiting and adjusting the criteria for financial aid to better match the evolving economic landscape.
Without a significant shift in state priorities, the cost issues that plague Ohio’s public universities will continue to spiral, leaving students with an ever-increasing financial hurdle that can discourage them from pursuing higher education altogether.
The Impact of Financial Stress on Academic and Personal Lives
It is important to take a closer look at how these financial barriers have a ripple effect beyond just the classroom. When students are forced to tackle the overwhelming burden of mounting debt or work excessive hours to cover basic expenses, the quality of their academic experience suffers.
Some of the subtle parts that point to academic and personal strain include:
- Academic Performance: Stress from financial insecurity often leads to lower grades and diminished academic output.
- Health and Well-Being: The constant worry about money can negatively affect mental and physical health, making it difficult for students to focus on their studies.
- Social Implications: Financial struggles can limit the ability to participate in extracurricular activities, internships, or networking opportunities—each of which plays a key role in overall career development.
In many ways, the full price of higher education goes well beyond the numbers on a tuition bill. The tricky parts of managing finances during formative years have lasting effects on personal development and long-term economic sustainability.
Addressing the Challenges: A Roadmap for Future Reforms
The current state of higher education affordability in Ohio requires a multi-faceted approach. Stakeholders—from state legislators and university administrators to students and community advocates—must work together to find creative solutions that can ease the financial burden for students.
Here is a roadmap of potential policy remedies and reform areas that could help alleviate the overwhelming challenges:
- Enhanced Funding Initiatives: Increase direct state investment in higher education budgets to reduce the reliance on tuition hikes.
- Revamping Financial Aid: Expand both need-based and merit-based programs to better assist hard-working students.
- Promoting Community College Pathways: Strengthen transfer agreements between community colleges and four-year institutions, ensuring a smoother transition and cost savings for students.
- Student Loan Reforms: Explore options to cap or restructure student loan interest rates to mitigate the long-term debt burden.
- Transparency and Accountability: Implement clear reporting mechanisms on how funds are distributed and used within public universities, boosting public confidence and ensuring that investments translate into improved affordability.
Each of these elements represents a small twist in the complex system of college funding that, when tackled collectively, could result in a meaningful transformation of the educational landscape in Ohio.
Community Involvement and Grassroots Advocacy
Finding your path through the maze of higher education reform is not solely the responsibility of state policymakers. Community involvement and grassroots advocacy play super important roles in pushing for change. Local organizations, parent groups, and student associations have a critical voice in demanding fairer pricing and increased state support.
Here are a few practical steps for community members:
- Engage with Local Leaders: Attend town halls and school board meetings to raise awareness of the affordability gap and advocate for budget increases.
- Form Alliances: Join or establish coalitions that unite students, educators, and community members with a shared goal of creating a more sustainable higher education system.
- Share Personal Stories: Amplify individual experiences with higher education costs to humanize the data and mobilize public support.
- Leverage Social Media: Utilize digital platforms to spread viable policy suggestions and rally community action around specific fiscal reforms.
When communities band together and push for improvements, their collective voice can steer through the conflicting priorities that often leave educational reforms on edge. Strong community advocacy helps ensure that the state’s approach to higher education is both comprehensive and sensitive to the needs of its residents.
The Future of Ohio’s Higher Education: Challenges and Opportunities
Looking ahead, the conversation about college affordability in Ohio is poised to become even more critical. As the state strives to balance its budget and meet the demands of a rapidly changing global economy, the pressure on public universities to keep their tuition at manageable levels will only intensify.
The following considerations are essential for mapping out a sustainable future:
- Innovative Funding Models: Explore alternative revenue models, such as public-private partnerships, targeted grants, and performance-based funding, to reduce the traditional reliance on tuition fees.
- Technology and Efficiency: Leverage technology to streamline administrative costs and operational inefficiencies, potentially lowering expenses that students indirectly pay for through tuition.
- Inclusivity in Decision-Making: Ensure that voices from all affected communities—especially those from lower-income groups—are included in the discussion on reforms.
- Long-Term Economic Planning: Recognize that investment in higher education is not just an expense but an investment in the state’s future workforce and economy.
These potential opportunities, if carefully implemented, could create a more balanced and accessible higher education system. It is crucial that state leaders remain committed to working through the challenging parts of budget reforms and channel the necessary resources into a lasting solution.
Resolving the Tangled Issues: Policy, Practice, and Partnership
In every state, there are twists and turns in the way educational funding is structured, and Ohio is no exception. The current scenario reflects a series of decisions and policies that need reexamination. Instead of letting the affordability gap widen, policymakers have the chance to figure a path toward reforms that embrace both practicality and equity.
An effective strategy might include:
- Regular Policy Reviews: Assess current funding mechanisms and financial aid packages with a view to continuous improvement.
- Transparent Reporting: Share detailed financial reports with the public so that stakeholders understand where each dollar is spent.
- Collaboration with Academic Institutions: Work closely with educational institutions to identify cost-saving opportunities that do not compromise academic quality.
- Emphasis on Long-Term Solutions: Focus on reforms that not only address immediate financial concerns but also set the stage for sustained support in the future.
This blend of policy innovation, community partnership, and institutional collaboration could help untangle the problematic knots that have long made higher education seem like a nerve-racking ordeal for many Ohio families.
Reflections on the Broader Economic Impact
The higher education crisis in Ohio serves as a microcosm for broader economic challenges facing the state. When students graduate with overwhelming debt, their ability to invest in their futures—whether through homeownership, starting a business, or contributing to local economies—is compromised. This situation not only affects individual lives but also the overall economic health of the community and the state.
In this context, the importance of affordable higher education extends far beyond campus walls. It influences workforce development, regional prosperity, and ultimately, the quality of life for all residents. As such, investing in education is not just a fiscal policy but a strategic imperative for building a resilient and inclusive economy.
Key reflections on the broader impact include:
- Workforce Readiness: Graduates with manageable debt loads are better positioned to contribute productively to the workforce.
- Economic Mobility: Affordable education opens doors for upward economic mobility, particularly for marginalized communities.
- Community Stability: When families are not overburdened by student debt, communities as a whole can thrive on stronger economic foundations.
Thus, reforming higher education funding is essential not only for the salvation of college affordability but also as a cornerstone for Ohio’s long-term economic stability.
The Role of Higher Education in Shaping Ohio’s Future
Education has always been a crucial foundation for societal progress. For Ohio, the current challenges in higher education affordability underscore a pivotal moment. The state stands at a crossroads where the right decisions could either entrench the status quo of financial inequity or pave the way for a more inclusive, equitable system that truly meets the needs of its diverse population.
If Ohio can resolve the tricky parts and navigate the tangled issues of funding, it may very well become a model for other regions grappling with similar challenges. The state’s future lies in its ability to adapt and innovate—not just for economic gain but for the betterment of every student’s journey.
To ensure that higher education remains a fair and accessible route to a promising future, stakeholders must be willing to take calculated risks, invest in long-term solutions, and work closely together. Collaboration between government, educational institutions, and community advocates is key to turning the current challenges into opportunities for meaningful progress.
Conclusion: A Call to Action for a Brighter Academic Future
In conclusion, the high cost of obtaining a bachelor’s degree at Ohio’s public universities, as illuminated by NCAN’s research, represents more than just financial figures—it reflects a system in urgent need of reform. The significant affordability gap not only hinders academic opportunities but also carries wider implications for the state’s economy, workforce development, and overall social mobility.
While community colleges serve as a promising alternative for those seeking a more affordable education, the long-term benefits of a bachelor’s degree remain a key driver of economic success. Therefore, a concerted effort to boost state funding, expand financial aid, and implement policy reforms is required to ensure that every student can pursue higher education without being overwhelmed by hidden complexity and costly financial burdens.
Ohio stands at a turning point. With deliberate leadership, community engagement, and innovative policy solutions, the state has the potential to transform its higher education landscape into one that is both fair and prosperous. By addressing the tricky parts of funding, the tied-up issues of tuition dependency, and the convoluted bits of financial aid, Ohio can set a new standard for accessible, affordable education.
The time to act is now. Let this editorial serve as a call to action for lawmakers, educators, parents, and students alike. Together, by finding our way through the intimidating maze of higher education costs and pushing for substantive reforms, we can lay the foundation for a brighter academic future in Ohio. Our children, our communities, and our collective future depend on it.
It is our hope that this discussion sparks the necessary debate and mobilization across all levels of society—one that leads to tangible changes and helps steer students toward success rather than into a web of crippling debt. The challenges may be many, with twists and turns that are both intimidating and nerve-racking, but with resolute determination and collaborative efforts, change is within reach.
Let us embrace this opportunity to reimagine a system where higher education is a stepping stone to greater achievements rather than a barrier. Ohio has the resources, the talent, and the community to overcome these obstacles. By working through the tangled issues and finding a fair solution, we can transform the landscape of higher education into one that truly serves the needs of every student.
We invite all stakeholders to join the conversation, support policy initiatives that encourage transparency and increased funding, and spread the word about the imperative need for change. With every contribution, whether big or small, we can move closer to an Ohio where higher education is a right, not a privilege defined by financial capability.
This editorial is more than an analysis—it is a vision. A vision of an Ohio where every student, regardless of background or economic status, can pursue higher education without fear of insurmountable financial hurdles. It is a vision that calls for action, collaboration, and above all, a reimagined commitment to the future of our communities and our state. Let us take this opportunity to work together, support our local institutions, and turn these challenges into avenues for lasting and equitable change.
Originally Post From https://signalcleveland.org/bachelors-degree-ohio-colleges-cost-more-great-lakes-states/
Read more about this topic at
The real crisis in Ohio schools isn’t money — it’s trust
Inside Ohio’s Higher Education Funding Crisis